What are Core Web Vitals? And what does this mean for your business and website?

User experience improvement is key to the long-term success of any website. Whether you are a site owner, marketer or developer, Web Vitals can help you measure a site’s performance and define opportunities for further improvement.
In November 2020, Google announced that beginning May 2021 Google Search page performance measurements will combine both Core Web Vitals and previous UX-related signals.
What is Core Web Vitals?
Google named "page experience signals" as Core Web Vitals. They have been officially added to the list of Google ranking factors.
Web Vitals has been implemented to provide a guide to the quality standards needed to achieve a positive user experience online.
Get Your Custom Price Quote Now!
Ready to find out the exact cost and delivery time for your project? Don't miss out on our special offer! Fill out our form to receive a personalized price quote and delivery time. Act now and secure the best deal! ⏰
How Web Vitals may affect your business and website functioning?
The Core Web Vital update aims at improving user interaction with your web site. Google measures such parameters as layout bias and visual stability to evaluate if user interactions were negative or positive. If a poor experience is detected (high bounce rate, low conversion rate, low site dwell, etc.), Google may reduce the page ranking in search layout. Understanding the features of Web Vitals as a ranking signal may help you enhance customer experience on your site and increase your site's ranking and performance in organic search.

Why are Web Vital Metrics so important?
As an IT company, Google’s main goal is to generate better search results. There are various ways to measure user experience and to include such parameters into Google's ranking algorithm to show the best related web pages. Basic web metrics are still important, and they focus on the user experience on one or another web page. If your web page is not validated by Google algorithms, your site may be ranked lower in the search results page, thus reducing the number of visitors and the income generated by the platform.
User experience is an important part of SEO
User experience (UX) and SEO work in synergy. The Web Vitals standards are aimed at optimizing visibility for site visitors and improving their experience with your site. Google's documentation defines UX metrics and introduces some standards of user experience on a particular web page. These metrics are page loading time, correct mobile content display, secured HTTPS, lack of intrusive ads, and page stability.
Core Web Vitals
The Core Web Vitals are a set of web page loading and display standards. They must be taken into account by all site owners and are included in all Google tools. Each Core Web indicator corresponds to one or another facet of user experience. Such metrics are measured in the field, and define actual user experience.
As the Internet evolves, the Core Web Vitals will be changing as well. As of 2021, the focus is on 3 basic metrics: loadability, interactivity, and visual stability. These 3 measure the following thresholds:
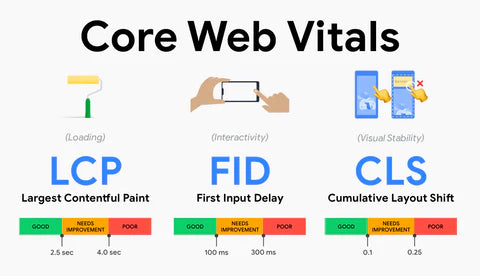
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) measures loading time. The LCP parameter must be less than 2.5 seconds page loading time.
First Input Delay (FID) measures interactivity. Web pages should achieve a FID of 100 milliseconds or less to provide a good user experience.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) defines visual stability. A web site should maintain a CLS of 0.1. or less.
LCP
LCP is a new Google metric that went live in May 2021. Maintaining Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) at a certain level is crucial to prevent your site from falling in search results.
Largest Contentful Paint is now considered the main rendering metric, and Google has added it to the list of the Page Experience factors.
What is the LCP?
LCP evaluates the time when the largest item on a given web page becomes visible in a browser.
LCP is a user-centric parameter, and the largest element on a web page is usually the most significant. Making it visible as quickly as possible improves the user experience.
The LCP searches for the largest element to get loaded throughout the process, and calculates the time taken to display that element. Examples of LCP items include a hero image or a text paragraph.
Why should we measure LCP?
LCP is a key parameter in the Web Vitals set of metrics as it defines the web page usage rate. It's also easy to optimize.
How does LCP affect SEO?
The Page Experience went live in June 2021, and LCP along with Cumulative Layout Shift and First Input Delay is used as an important ranking factor in mobile search output.
Meeting the recommended values for all 3 parameters determines if an icon will appear next to your site name in the search results list. This would have a significant impact on clicking rates!
Google's goal is to load pages quickly and smoothly on mobile devices and desktops. Once LCP is taken into account, this metric starts affecting the search position.
LCP impacts UX. The better the UX, the lower the bounce rate and the higher your search ranking position.
Elements that may affect LCP:
Images
Background images
Videos
Fonts
Even if you don't care about the Core Web Vitals as a search position ranking factor, we still recommend tuning the LCP when improving your site's performance.
Google created the LCP metric as it correlates well with user behavior measurements. If you're stuck improving conversion rates, time spent on the page, or any other behavioral factors that may impact your business, improving the rendering performance will definitely help you.
CLS
Cumulative Layout Shifts is a new Google ranking parameter. It describes how users perceive a site's performance.
Have you ever experienced sudden changes to your web page while browsing? Without a warning, text may be shifted, making you lose the point where you were reading. Even worse, a button may move away, making you click on something completely different.
Elements that sometimes may cause a shift include fonts, images, videos, contact forms, or buttons. While this can be annoying to a user, in some cases it can lead to serious troubles with the page.
CLS shifts web elements as the page loads, allowing the page to run smoothly on all devices. A low CLS score indicates that problems with the code have been resolved.
Why does CLS occur?
According to the datasheet from Google, five reasons are causing Cumulative Layout Shift:
Images
Dynamically embedded content.
Web fonts calling FOIT/FOUT.
Actions waiting for response before DOM update.
How does CLS affect SEO?
SEO success includes increased rankings, traffic, conversions, and revenue growth. A good user experience is key to an outstanding search engine optimization results.
According to Screaming Frog Research, only 47% of desktop URLs and 46% of mobile URLs reach good CLS scores. The average CLS score is 0.29 for mobile and only 0.25 for desktop. Taking these low scores into account, it is obvious that CLS assistance is necessary to improve site's performance in order to provide a consistent user experience and achieve better SEO results.
In summary, a Google ranking factor called Cumulative Layout Shift has officially been added to search engine optimization. Chrome now measures user experience and visual stability (CLS) when content shifts unexpectedly due to technical reasons on a site.
A good CLS score will improve the user experience by eliminating layout shifts and other user experience flaws. Another important reason for a good CLS is to increase SEO and improve search ranking position, conversions, leads and revenue.
FID
We know that first impressions matter a lot, whether online or offline.
On the Internet, the first impression plays a crucial role in turning a new visitor into a regular one or making them leave and never come back. But what is a good impression? How to know if your site creates a positive impression on users?
First impressions online can be formed differently. It may be a convenient web site's design, its visual appeal or maybe its speed and responsiveness.
First Input Delay (FID) parameter measures user's first impression, site's interactivity and responsiveness.
What is the First Input Delay?
First Input Delay (FID) is a real-world user web performance metric which tracks time from the moment a user starts interacting with a web site until the browser begins processing that interaction (click, mouse move, key input, etc.).
Simply put, FID is a delay between the moment you click or tap on an element (a link or button), and the moment the browser responds to your action and starts processing it.
Why does FID occur?
While we often assume that a web site responds immediately to our click, in most cases, we experience the opposite - we load a web page on our phone, but we get frustrated when nothing happens.
The delay is due to many reasons, particularly overloaded sites with heavy content such as sliders, analytics scripts, ads, or video content. Before you visit any site, the browser needs time to complete a huge amount of tasks. Big pictures, videos or analytics scripts may slow sites down, so you may experience a "frozen" site issue. When you try to press on the menu button but nothing happens, your click may simply be queued up, and only after all other resources on the page are loaded, your menu will open. This creates a negative user experience, leaving users frustrated. If the site is down, users will simply close it and never come back.
Does FID affect SEO?
Undoubtedly, FID affects SEO. In our opinion, it has the highest impact compared to all other metrics. As mentioned above, a site that doesn't respond to a user's clicks creates a negative impression. It's even worse when the user does not possess a new iPhone, but an old Android smartphone, and without a reliable Internet connection. In these cases, it may take forever to get a web page loaded. The user gets no response, and consequently any interaction with a site is out of the question, they close the site and search for another one. At this point, Google detects that the dwell time on the site was low, and begins to lower the site's position in the search output ranking. All this certainly affects the conversion, since users simply cannot reach the product page or shopping cart, due to poor site's performance.
The first input delay (FID) is a user's feedback to the responsiveness of your web page. First impressions are critical in forming an overall impression of a site's quality and reliability.
Get Your Custom Price Quote Now!
Ready to find out the exact cost and delivery time for your project? Don't miss out on our special offer! Fill out our form to receive a personalized price quote and delivery time. Act now and secure the best deal! ⏰




